
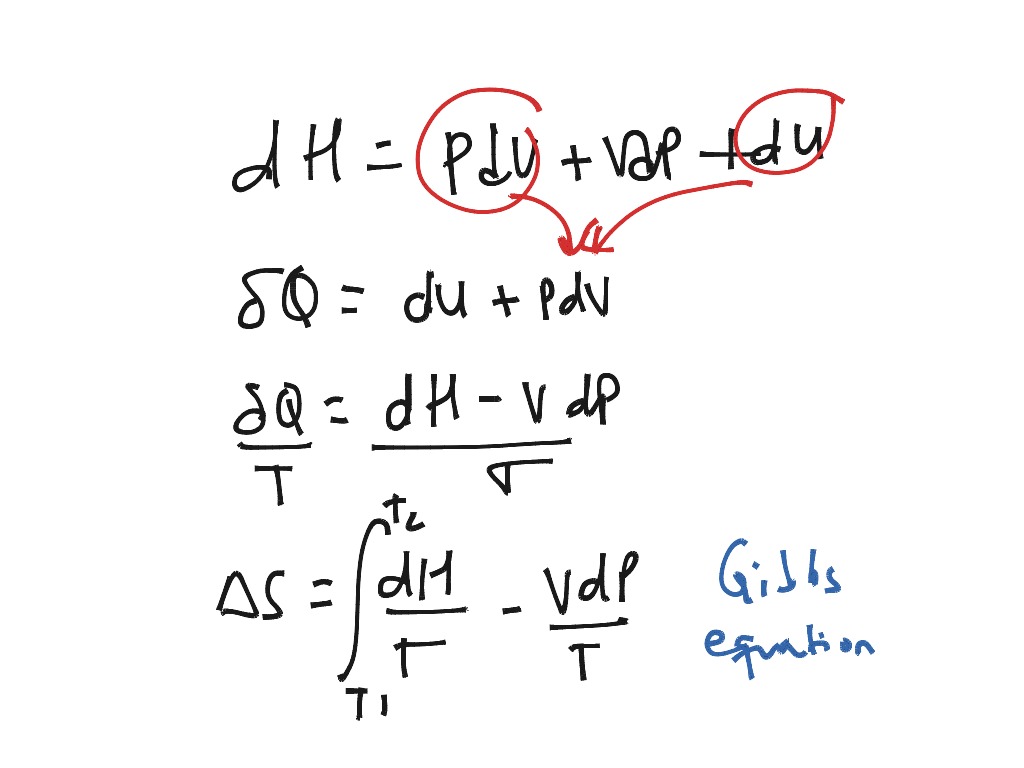
Is the part of that energy that goes into doing work. U is the energy input to the system, and W System ( W, such as a hot gas pushing against a piston in Some of that energy could easily be expressedĪs an amount of mechanical work done by the Goes into the internal heat content, Q, making Q a Suppose you pumpĮnergy, U, into a system, what happens? Part of the energy This idea can lead us toĪn alternate form for equation 2, that will be useful later on. Is a negative number), then the entropy will go down too.Ĭlausius and the others, especially Carnot, were much interested in the ability toĬonvert mechanical work into heat energy, and vice versa. Goes up, while the temperature remains fixed, then the entropy S goes up.Īnd, if the internal heat energy Q goes down ( Q Is positive, then so is S, so if the internal heat energy That S indicates a "change" or "increment" inĪnd S 2 are the entropies of two different equilibrium states, Here the symbol " " is a representation of a finite increment, so To differentiate equation 1, and arrive at equation 2. In classical thermodynamics is defined only for systems which are in thermodynamicĪs long as the temperature is therefore a constant, it's a simple enough exercise Simultaneous temperatures) if it is in thermodynamic equilibrium. Of entropy, and a system can only have "a" temperature (as opposed to several The temperature of the system is an explicit part of this classical definition Out that what they called heat content, we would now more commonly call Ludwig Boltzmann, but we will cover that story later. The molecular theory became predominant, mostly due to Maxwell, Thomson and In which mechanical work could be converted into heat. That this could not be the case, because it was inconsistent with the manner

It was Thomson who seems to have been the first to explicity recognize Heat as a kind of fluid, a conserved quantity that moved from one system to the Their average kinetic energy, had not yet appeared. The idea of a gas being made up of tiny molecules, and temperature representing Of the system, and T is the temperature of the system. In equation 1, S is the entropy, Q is the heat content The specific definition, whichĬomes from Clausius, is as shown in equation 1 below. ( On Different Forms of the Fundamental Equations of the Mechanical Theory of Heat, 1865 Mathematical & physical quantity, with well understood applications.Ĭlassical thermodynamics developed during the 19th century, its primary architects beingīut it was Clausius who first explicitly advanced the idea of entropy In all of these cases, not as some fuzzy, ill-defined concept, but rather as a clearly defined, My goal here is to shwo how entropy works, Much of what we now call information theory. Shannon to borrow the Boltzmann-Gibbs formulation of entropy, for use in his own work, inventing
Mechanics in the late 1800's created a new look for entropy. There is no such thing as an "entropy",Įntropy was born as a state variable in classical thermodynamics. That entropy is what the equations define it to be. That means thatĮntropy is not something that is fundamentally intuitive, but something that is fundamentallyĭefined via an equation, via mathematics applied to physics. But it should be remembered that entropy, an idea born fromĬlassical thermodynamics, is a quantitative entity, and not a qualitative one. With articles, papers, books, and various & sundry other sources, filled to overflowing with


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
